“Risk Management is not about future decisions, but about future of decisions that we must take now”
Rabert N. Charette
Risk is an integral part of life and inevitable. We need to differentiate between positive and negative risks. A positive risk can be an opportunity for the organization and we must have information for positive risk along with negative risk,and it can be perform through SWOT analysis. I can recall quote from my previous organization’s boss Mr. Sandeep Chopra that ; “in each and every step risk is involved we need to understand the how critical risk is? and have action plan to mitigate those risks.if we are working in steel plant we need to work with fire and we need to live with that”.
In our current industries this is one of regulatory requirement that we must have risk management for our processes, design, services and system. There are multiple guidelines which talks about Risk management through a systematic approcah. Major guidelines are ICH Q9(Quality Risk Management), ISO 9001:2015, PMP 6.0 etc.I would try to show some of steps involved in those guidelines.
It is commonly understood that risk is defined as the combination of the probability of occurrence of harm and severity of that harm.Quality Risk management is “a systematic process for the assessment, control, communication and review of risks to the quality of the product across the product life cycle”
The basic steps involved in Risk management is common among all the guidelines with minor differences for calculation of risk.
- Risk Identification :Checklist to be prepared for identification
- Risk Analysis :Estimation of risk associated with identified hazard
- Risk Evaluation(Prioritization): RPN Calculations
- Risk Control(Mitigation Plan):Action plan
- Risk Communications: Communications to stakeholder
- Risk Review: Maintain Risk Register and timely update
ICH Q9 is backbone for pharmaceutical industries to conduct risk assessment and below tree a representation for quality risk management. Generally Q8, Q9 and Q10 works together because it involves life cycle of drug product and Quality management system(QMS) and when it combines with risk associated with product life cycles and how are you going to control through available resources(QMS)

In PMP 6.0 the tools and techniques are given below. As per section 11.0

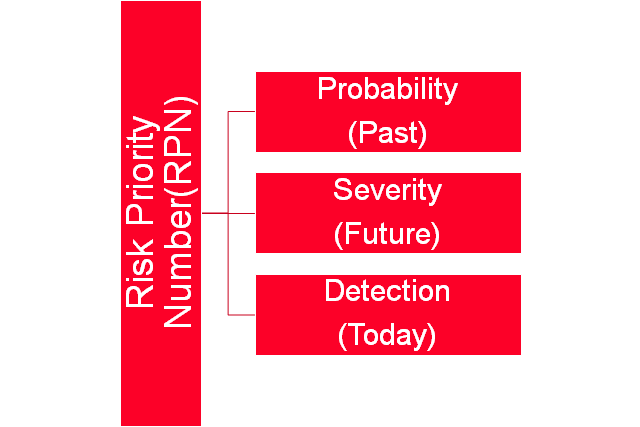
Risk management can be qualitative or quantitative and different tools are used for calculating risk scores. RPN number is multiplication of Probability, Detection and Severity.The tools mostly used are brainstorming, Ishikawa diagram, Flow charts for qualitative analysis. For quantitative analysis Monte Carlo, FMEA etc.
Monte Carlo analysis is a decision-making and problem-solving tool used to evaluate a large number of possible scenarios of a process. Each scenario represents one possible set of values for each of the variables of the process and the calculation of those variables using the transfer function to produce an outcome Y. By repeating this method many times, you can develop a distribution for the overall process performance. Monte Carlo can be used in such broad areas as finance, commercial quality, engineering design, manufacturing, and process design and improvement. Monte Carlo can be used with any type of distribution; its value comes from the increased knowledge we gain in terms of variation of the output.Performing a Monte Carlo analysis is one way to understand the variation that naturally exists in your process. One of the ways to reduce defects is to decrease the output variation. Monte Carlo focuses on understanding what variations exist in the input Xs in order to reduce the variation in output Y.
Failure Mode Effects Analysis(FMEA): This is well established tool used in any kind of industries follows the common steps: identification,assessment,Control and monitoring throughout product life cycle.Its a dynamic document and shall be updated any step added or removed during its life cycle. Basically FMEA involves pre and post calculation of RPN and priortization of identified risk and Corrective action to control(reduce /accept-avoid, mitigate,transfer) risks. RPN is calculated be multiplying Probability, severity and detection. Selection of risk depends on high RPN number and shall have action plan based on priority and available resources.
I am attaching a FMEA template for easy understanding of tool.


